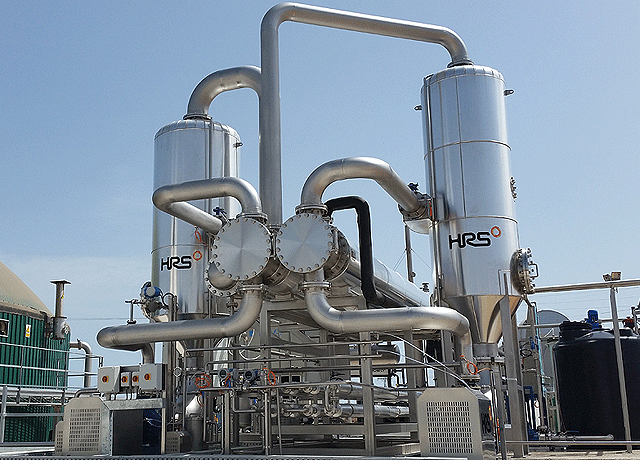
Evaporation & Concentration of Environmental Waste Streams
Evaporation is a proven and effective way of reducing the volume of many waste streams.
HRS Heat Exchangers offer solutions for the evaporation and concentration of waste streams from a wide variety of industries, such as water treatment, bioenergy and food production.
A common issue when treating certain waste streams with standard evaporation technologies (such as falling film) is that when heated, they can foul equipment. As the concentration of solids increases during the evaporation process, so does the risk of fouling; which then results in lower rates of heat transfer and lower efficiencies. Fouled evaporators need regular cleaning which further reduces operating efficiency.
HRS Heat Exchangers overcomes these fouling issues by using corrugated tube heat exchangers (such as our K Series) or scraped surface heat exchangers. As an example, the Unicus Series scraped surface evaporator can guarantee fouling-free operation in large capacity installations. For more details of the range of suitable products, please visit our heat exchangers page.
Please fill in the form with as much as information so that we can attend to your query appropriately.
Note that fields marked with * are mandatory.
Download HRS Brochure here.
Address:
HRS Process Technology Inc
840 Kennesaw Ave.
NW B-1, Marietta
Atlanta, GA 30060
United States
Email: info@us.hrs-he.com
Tel : +1 770 726 3540
Enquire today for a free quote
FORCED RECIRCULATION
In most situations, HRS evaporators will use forced recirculation. By pumping the fluid through the evaporator at a much faster flow rate than the evaporator feed. This maintains a high velocity in the fluid, resulting in high heat transfer coefficients which increase the efficiency of the process. Forced recirculation is particularly useful when handling viscous fluids which would otherwise suffer from poor heat transfer at higher flow rates. In such cases using a recirculating pump maintains heat transfer high and keeps the evaporator design relatively small.
MULTI-EFFECT EVAPORATION
In multi-effect evaporation, the evaporated water from the first effect (or evaporation process) is used as the heating media in the second effect, meaning less energy is required. This process can be repeated several times to maximize energy efficiency. This method means that, for example 2 lbs of steam invested can evaporate several lbs of steam from the product. HRS Heat Exchangers uses multi-effect evaporation wherever possible. Combinations of multi-effect evaporation and steam compression (mechanical vapor recompression or thermo-compression) can be supplied to further increase energy efficiency.
INTEGRATION WITH DRYER PLANT
Another way optimizing energy use is to combine the evaporator with a dryer plant. This solution works well where a waste stream is separated into a solid- and liquid phase by mechanical separation, such as a centrifuge or a decanter. The solid phase is sent to an indirect dryer, while the liquid phase is sent to the evaporator.
Evaporated water from the dryer is used to heat the evaporator, while the concentrate from the evaporator is mixed with the solid phase prior to sending it to the dryer. This design provides the biggest reduction in the volume of the waste in the most energy efficient way.
HRS evaporation and concentration systems are suitable for the following applications:
Environmental applications:
- Brine
- Wastewater treatment
- Manure
- Sludge
- Other effluents
Bioenergy applications:
- Digestate from biogas production
- By-products from bioethanol production
Food & agricultural applications:
- Food and agricultural wastes
- Fruit concentrate